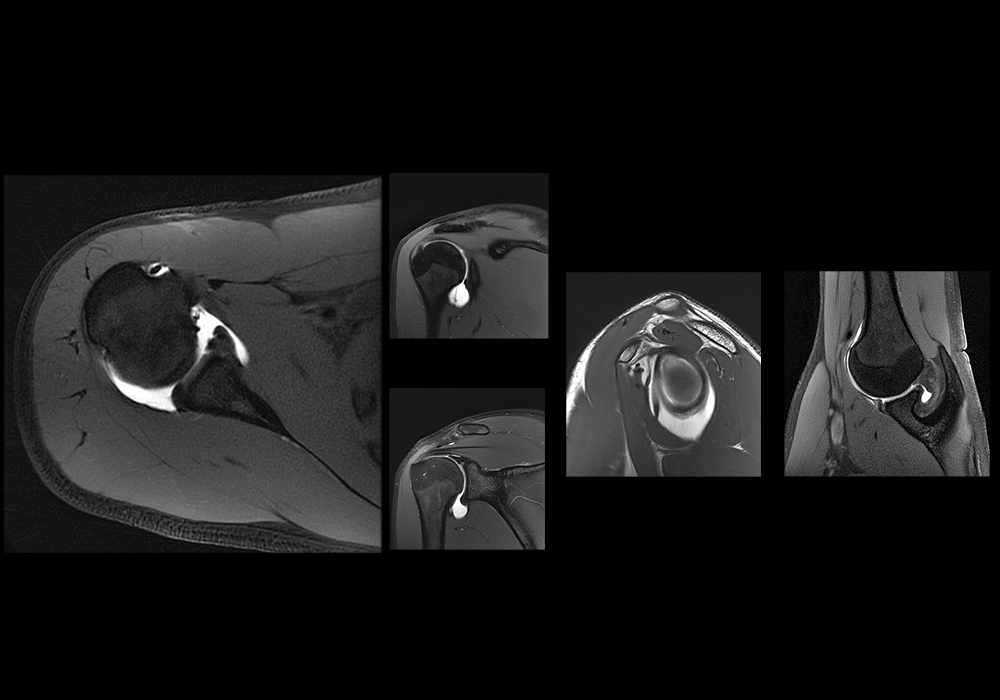
MR (Magnetic Resonance) arthrography of the shoulder: normal anatomy
Preamble
The present document contains important information on the conditions (hereinafter "Conditions") of subscription to the paid services available on the site, accessible at www.imaios.cn (hereinafter "Site") or offered in the applications, available on the Apple Store and Android platforms (hereinafter "Applications") and published by the company IMAIOS (Shanghai) Information Consulting Co., Ltd. (hereinafter “IMAIOS” or "Publisher" or "Licensor"). In this respect, as the Applications are available on these platforms, the Customer using the Applications shall also be required to accept the terms of use of the Apple Store or Android platforms. The Conditions are reserved solely for consumers, as defined by law and jurisprudence, acting exclusively on their own behalf. In accordance with the laws of the People’s Republic of China (the “PRC”), the essential characteristics and prices of the Paid Services are available on the Site and the Applications.
The Conditions are accessible, before any order and before its completion on the Site and on the Applications.
Publisher identification
Company name: IMAIOS (Shanghai) Information Consulting Co., Ltd.
Corporate form: Limited liability company
Registered office: Room 1578, Building 2, 1266 Nanjing West Road, Jing'an District, Shanghai, 200040, China
Unified Social Credit Code: 91310000MAE3FRX513
Legal representative: Nguyen-Thanh Denis HOA
Email: contact@imaios.cn
1. Purpose of the contract
1.1 Definitions
For the purposes of this contract, the terms below are defined as follow:
"License" refers to this License agreement defining the conditions of access and use of the Products imposed by the Publisher that the Customer accepts in order to place an order. According to the terms of this License, the Editor grants the Customer a license to use the Software for internal purposes as well as for its own needs. This term refers to the present contract, its annexes and its successive modifications.
"Licensee" or "Customer" or "User": means the natural person wishing to access and use the Paid Services offered by IMAIOS under the conditions set forth in this license, acting in his or her own name.
"Software" or “Solution” means original Software (including but not limited to, e-Anatomy and vet-Anatomy) published and distributed by IMAIOS and for which the Licensee wishes to have access to paying functionalities. This original Software is based on intangible elements and components such as the development of a source code, a set of instructions, programs (such as graphic interface, databases, etc.), processes and rules which are the result of specific and creative choices and above all of intellectual contribution. It also means the documentation associated with said products and their accessories (images, texts, etc.), i.e. any element attached to or associated with the Software that allows their functioning and use.
"Paid Services": refers to paid access to features of the Software, available on the Site or within the Applications. The Licensor hereby grants the Licensee, who accepts it, a non-exclusive, non-transferable, non-assignable, revocable license to use the paid-for software features ordered for the entire duration of this License, in accordance with its intended purpose and for its personal needs only.
1.2 Purpose
The purpose of this contract is thus to determine the conditions of subscription by the Customer allowing him to use the Paid Services of the Products, accessible from the Site or the Applications, within the limits of use defined in the License.
1.3 Scope
The Licensee declares that he has read the documentation freely accessible on the IMAIOS website, which presents the characteristics of the Software, as well as the terms and conditions of the License granted by the Publisher to the Customer for the Software and, in the event of an order placed on the Apple Store or Android platforms, the related terms of use.
The Licensee acknowledges that the granted use only allows the Software to be consulted on the Website or within the Applications downloaded onto the mobile device (tablet, telephone) belonging to the Licensee. The Licensee agrees that this License does not include any additional services other than the Paid Services "defined" in Article 1.1 "Definitions". This License does not authorize the Licensee to grant sub-licenses.
This License does not include user support for the Licensee.
Licensee hereby agrees that the Software contains proprietary content, information and materials that are protected by applicable intellectual property and other laws, including but not limited to copyright, and that Licensee shall not use such proprietary content, information or materials in any manner whatsoever, except for the permitted use of the Software under the terms of this Agreement.
The Licensor's intellectual property rights in trademarks, designs and models are not within the scope of this License.
2. Terms of order
In order to subscribe to Paid Services, the Customer must follow the steps below:
2.1. On the Site
a. The Customer will click on a link or type in the address of the Site.
b. The Customer will follow the instructions of the Site and in particular, the instructions necessary for the registration of the Customer, reflected by the creation of a User account if he does not already have one: in this case, the Customer will have, in particular, to provide information relating to his title, his name, his first name, his billing address, e-mail address and phone number. The Customer agrees to provide true and accurate information. The Customer may, at any time, modify his personal information, his login and password, by accessing his account. The Customer is the only one responsible for the use of his login and password, which he agrees to keep secret. In case of loss or unauthorized use of his account, it is up to the Customer to inform the Publisher without delay, by using the tab "Contact" present on all the pages of the Site. In the event of a possible loss of the password, when opening the session and entering the username and password, the Customer can click on a link that will allow him to ask the Publisher to grant him a new password that will be sent to the address indicated in his personal information.
c. From then on, the Customer will read the present on the link "Subscription Terms & Conditions" as well as the conditions of access and use of the site and the applications. The Customer will then check the box "I accept the Subscription Terms & Conditions and Conditions of access & use".
d. It is then up to the Customer who wishes to access the Paid Services to fill in the order form. In the event of prolonged inactivity during the connection, it is possible that the selection of the Paid Services chosen by the Customer before this inactivity is no longer guaranteed. The Customer is then invited to restart the selection of the Paid Services from the beginning. The Customer will check the elements of the order and, if necessary, identify and correct any errors; it is always possible to abandon the order until confirmation.
e. The Customer will confirm the order and follow the instructions of the Payment Service Provider to pay the Total Price.
f. The Customer will be redirected to the "My Order" page. At the same time, the Customer will receive an electronic order confirmation, showing the order number and the price paid. The Customer will be able to access an invoice in electronic format on his account. It is recommended to print the order confirmation page, in order to keep the elements of the order, as well as the order number. This number must be remembered for any claim.
2.2 On Applications
a. The Customer shall go to the Application, or, if he does not already have it, to the Apple Store or Android platforms in order to download the Application, in accordance with the terms and conditions applicable to the relevant platform and agreeing to abide by the conditions of access and use of the site and the Applications.
b. The Customer must create a User account within the Application, in order to be able to benefit from the Paid Services on other devices, such as on the Site or the same application on another platform. To this end, he must provide information such as his title, name, first name, billing address, e-mail address and phone number. The Customer agrees to provide true and accurate information. The Customer may, at any time, modify his personal information, his login and password, by accessing his account. The Customer is the only one responsible for the use of his login and password, which he agrees to keep secret. In case of loss or unauthorized use of his account, it is the Customer's responsibility to notify the Publisher without delay, using the "Contact" tab in the Applications. In the event of a lost password, when logging in and entering the username and password, the Customer may click on a link that will lead the Publisher to grant a new password which will be sent to the Customer at the address indicated in his personal information.
c. In any case, the subscription to the Paid Services is made with the platform. Therefore, in addition to reading these terms and conditions on the "Subscription Terms" link, as well as the terms and conditions of access and use of the website and applications, and checking the box "I accept the Subscription Terms & Conditions and Conditions of access & use", the Customer will also be bound by the general terms and conditions of the Apple Store, Android platforms or Payment Service Provider, which he will have already read when downloading the Application and which he will be required to accept again.
d. It is then up to the Customer who wishes to access the Paid Services to order the desired services by selecting the services, clicking on "Subscribe" and then on the desired subscription and on "Subscribe". The Customer will then validate his order, according to the terms retained by the platform and will follow the platform's instructions to pay the price.
e. The Customer shall receive an electronic order confirmation without delay, showing the order number and the price paid. The Customer will be able to access an invoice in electronic format on his account within the platform. It is recommended to keep the order confirmation page, in order to keep the elements composing the order, as well as the order number. This number must be mentioned for any claim.
3. Access to Paid Services and Withdrawal
3.1 Access and Limitation
Access to the Paid Services on the Site will be activated after validation and payment of the order, by providing a username and password. The Customer will be able to access, by logging in on the Site, the Paid Services ordered and paid for. Access to the Paid Services on the Applications occurs after payment has been made on the Application, on the Customer's Android platforms, Apple Store or Payment Service Provider account, but can also be done by linking, within the Application, to the account opened on the Site in order to benefit from the paid services that have been subscribed to on the Site. Indeed, while the use of the Customer's account is strictly individual, no account sharing being accepted, the Customer is entitled to use, in a non-simultaneous manner, the Paid Services on several devices, on the basis of a single subscription.
The Licensee acknowledges that the use of the Paid Services does not include any installation, adaptation, customization, or training services: such services, if required, will be billed separately upon request by the Licensee to the Licensor.
3.2 Withdrawal
Concerning the orders made on the Site, the Customer benefits, beyond even the legal prescriptions, from a right of retraction of 30 (thirty) days from the day his order has been completed. The Customer can thus during this period, without attesting to any reason, go back on his commitment by sending to the Publisher, ideally with acknowledgement of receipt, a letter or an e-mail in that sense and without any ambiguity. A standard withdrawal form, which is only an example, is communicated to the Customer in the appendix. The refund will then take place within 14 (fourteen) days.
With respect to orders for Paid Services placed on the Applications, Android platforms, Payment Service Provider or Apple Store terms of use apply.
In this respect, the Customer ordering services on the Apple Store as well as on Android platforms expressly acknowledges, due to the nature of the subject matter of the contract (access to and use of Products requested by the Customer prior to any exercise of a right of withdrawal), that withdrawal is excluded when the download of the Paid Services takes place at the time of the order on the Apple Store and that the services ordered on Android platforms or Payment Service providers are also immediately available.
During the realization of the various stages mentioned above of the order, the Customer commits himself to respect the present contractual conditions.
The Publisher reserves the right to refuse the order for any legitimate reason and in particular if it is abnormal, placed in bad faith or when there is a dispute with the Customer concerning the payment of a previous order.
4. Price and payment
4.1 Price
To access and use the Paid Services, the Customer must pay the price corresponding to the service in question and to the duration of the subscription chosen.
The price of the subscription allowing access to and use of the Paid Services is specified on the current price list available on the Site or on the Application and mentioned again at the time of the order; it includes all taxes.
The Paid Services correspond to:
· the cost of granting this License for the use of the Site and Applications;
· if applicable, the cost of support, usage statistics, hosting, and bandwidth for the use of the Software.
All other services are not included in the Price, including any potential installation, adaptation, customization or training fees: such services, if required, will be billed separately upon request by the Licensee to the Licensor. In this regard, the telecommunication fees related to access to the Site or the Application shall remain the sole responsibility of the Client. The validity period of the offers and prices is determined by the updating of the Site and the Applications.
4.2 Payment
On the Site and Applications, the payment of the total price by the Customer is carried out by credit card or debit cards, Apple Pay, WeChat Pay or Alipay via third party Payment Processing Providers. The accepted credit or debit cards are those supported by the third parties payment processing providers
Where applicable, the transaction is immediately debited from the Customer's digital wallet or bank card after verification of the card's data, upon receipt of the debit authorization from the company issuing the digital wallet or bank card used by the Customer.
The commitment to pay by means of a digital wallet or payment card is irrevocable. By providing his digital wallet or credit card information, the Customer authorizes the payment provider to debit his digital wallet or credit card for the amount corresponding to the total price.
To this end, the Customer confirms that he is the holder of the digital wallet or bank card to be debited and that the name on the bank card is indeed his. The Customer communicates the sixteen digits and the expiry date of his credit card as well as, if necessary, the numbers of the visual cryptogram.
In the event that it is impossible to debit the total price, the order will be immediately canceled by right.
The Licensor makes every effort to ensure the confidentiality and security of data transmitted on the Site. The Customer is informed that when paying by digital wallet or credit card, the Licensor uses the services of a service provider who is responsible for ensuring the safety of the payment transaction; the Publisher does not have access to the Customer's credit card numbers which are not stored at the Publisher but at the payment provider. Moreover, when subscribing to paid Services on the Applications, the Publisher does not handle the payment operations, which depend on the platforms or Payment Service Provider.
5. Duration of access and renewal
Access to the Paid Services begins on the day of payment of the order for the duration chosen by the Customer when ordering. For certain Paid Services, individual subscriptions are automatically renewed on the expiration date; the user may at any time, up to and including the day before the renewal, disable this renewal from the interface of his profile, under the section "Subscriptions", or, in the context of the Applications, on the page for managing purchases and/or subscriptions provided by Apple Store (Settings > Apple ID), Android platforms or Payment Service Provider.
The User will be informed of the deadline for objecting to the renewal of the subscription by e-mail, at the earliest 3 months and at the latest 1 month before the annual subscription renewal date.
It is expressly agreed between the Parties that IMAIOS reserves the right to modify its rates and access conditions from one period to another.
In addition, certain Paid Services may be subscribed to for an indefinite period: IMAIOS may not request a new paid subscription for these services, but does not commit to ensuring that these services, or the Application on which they are located, remain available.
6. Applicable contract documents
By using the IMAIOS’ Site and the Applications, the Licensee accepts, without reservation, the Conditions of access and use of the Site and Applications available on the IMAIOS site in free access and on each Application, as well as the Licensor's Privacy Policy. In the event of a conflict between the general terms of use and the present contract, the latter shall prevail. Furthermore, the Customer using the Applications is subject to the terms of use of the platform used, namely Android platforms, Payment Service Provider or Apple Store. In the event of a conflict between those conditions and the present terms and conditions, the latter shall prevail.
7. Termination
In the event of a breach by either party of any of its contractual obligations, this agreement may be terminated at the request of the injured party, in the absence of an amicable agreement, after formal notice to perform has been served by registered letter with acknowledgement of receipt which has remained unsuccessful for a period of thirty days, simply by sending a registered letter with acknowledgement of receipt notifying said termination. In the event that the Licensee fails to comply with its obligations, no refund of the price paid, corresponding to the remaining period of the subscription, will be granted.
8. Miscellaneous provisions
Unless proven otherwise, the data recorded on the page "My Account" of the Site constitutes proof of all Orders placed on the Site, and the Customer may thus access the history of orders placed at any time. Similarly, orders placed on the Applications are visible on the Apple Store, Android or Payment Service Provider platforms.
The Customer may access the contracts binding the parties at the time of the order (Subscription Conditions, Privacy Policy, Terms and conditions of access and use of the Site and Applications) on the Site and via links within the Applications. The Customer may download these contracts and keep them in a durable manner on any other medium of his choice.
This Agreement shall be binding upon and inure to the benefit of the parties and their respective successors in interest. Licensee may not assign its rights, obligations or privileges hereunder or under any law, except with the prior written consent of Licensor.
The translation of the Conditions into any other language is provided for information purposes only. In the event of any inconsistency between the translated version and the English version, the English version shall prevail and be the only version that is binding on both parties and governs the relationship with the Publisher.
This contract and its interpretation are subject to the PRC law and the parties acknowledge the exclusive jurisdiction of the people’s court in Shanghai at the place where the Publisher is registered at.
Cancellation form template
(for Orders placed on the Site)
IMAIOS (Shanghai) Information Consulting Co., Ltd.Room 1578, Building 2, 1266 Nanjing West Road, Jing'an District, Shanghai, 200040, China
I hereby inform you of my decision to exercise my right of withdrawal for:
the order n°XXXX, concerning the service XXXX, made on XX/XX/202X.
Consequently, I would like to ask you to return to me as soon as possible and at the latest within 14 days following the reception of the present, the sum of .... CNY that I paid to you at the time of my order, this in accordance with the provisions of the PRC Civil Code.
Name of the consumer
Address and, if necessary, email address of the consumer
Date
Warning to be read carefully
1. This document contains important information about the terms and conditions (hereinafter "Conditions") for accessing and using the site accessible at www.imaios.cn (hereinafter "Site") and the applications, including but not limited to, e-Anatomy and vet-Anatomy available on Android and Apple Store (hereinafter "Applications"), which apply between the company that publishes the Site and the Applications and all the users of the Site and Applications (hereinafter referred to as the "User").
2. The Site and the Applications may only be used for informational purposes. The Site and the Applications are intended only for use by knowledgeable healthcare professionals and those who are already engaged in a training process, independent of the Site and the Applications, to become professionals.
The Site and the Applications can in no way answer the public's medical questions. They are not intended to replace the relationship between the patient and his health care professional or to replace his medical advice. The Site and the Applications have not been tested or approved for clinical use. They are not medical devices and are not certified as such. They may not be used as diagnostic tools.
In general, we recommend that you systematically seek the advice of your usual doctor before consulting any Internet sites and applications with medical content.
3. By accessing the Site or the Applications and their content, or by using any of the services offered on the Site and within the Applications, you fully and unreservedly accept these Conditions as defined below and you declare that you are bound by these Conditions for an indefinite period of time, whether or not you are a healthcare professional. They include various limitations and exclusions of liability, as well as a jurisdictional clause governing the handling of any dispute.
By accessing the Site or downloading one of the Applications, you acknowledge that you are aware of the Privacy and Data Protection Policy practiced by the Editor and accessible at https://www.imaios.cn/en/privacy-policy, on any page of the Site and within each Application. You declare that you do not object to this Privacy and Data Protection Policy implemented by the Editor.
4. These terms are subject to change at any time and without notice; they are systematically brought to the attention of any person accessing the Site or an Application by a link accessible on all pages of the Site and within each Application. We therefore thank you for regularly consulting these terms and their update.
If you do not accept all or part of the Conditions, you are requested to renounce all use of the Site and the Applications and to leave them.
5. These terms apply exclusively to your access to and use of the Site and the Applications; they do not alter the terms or conditions of any other agreement you may have with the Editor.
1 PRESENTATION OF THE SITE AND THE APPLICATIONS
1.1 Description and objectives of the Site and the Applications
Both the Site and the Applications are intended exclusively for an audience of knowledgeable healthcare professionals(hereinafter "User(s)"). They are designed for educational purposes and contain medical information (articles, illustrations, tools and other resources, etc.).
1.2 Origin of the Site and the Applications
The Site and the Applications are published by the company IMAIOS (Shanghai) Information Consulting Co., Ltd. , Room 1578, Building 2, 1266 Nanjing West Road, Jing'an District, Shanghai, 200040, China (hereinafter referred to as the "Editor").
The director of the publication is Mr Denis Hoa.
1.3 Hosting of the Site
The Site is hosted by AWS China (Ningxia) Region, operated by Ningxia Western Cloud Data Technology Co. Ltd. (NWCD).
1.4 Regular contributors
All members of the IMAIOS team contribute regularly to the provision of medical information on the Site and the Applications, and in particular its managers:
Denis Hoa, Doctor of Medicine, graduate of the Faculty of Medicine of Montpellier, DES Radiodiagnostic et Imagerie médicale, Laureate of the Faculty of Medicine of Montpellier, Holder of a Master 2 Recherche en Radiophysique et Imagerie médicales, and
Antoine Micheau, Doctor of Medicine, graduate of the Faculty of Medicine of Montpellier, DES Radiodiagnostic et Imagerie médicale.
1.5 Financing of the Site and the Applications
The Site is financed by the Editor and the Users' subscriptions. The Applications are financed by the Editor and by the integrated purchases made by the Users, the Applications being of freemium type.
The shareholders of the Editor have no direct or indirect link with the pharmaceutical industry.
2 ACCESS TO THE SITE AND APPLICATIONS
2.1 Open access and registration
2.1.1 The Site
The Site is free and in free access. However, the Editor reserves the right to make access to all or part of the Site subject to payment, unilaterally and without prior notice.
Access to certain areas of the Site may be subject to prior registration according to a procedure explained on this occasion. If necessary, the Editor reserves the right to suspend, limit or refuse access to the Site, unilaterally and without prior notice, to any registered User (hereinafter "Registered User") who does not respect the Conditions.
2.1.2 The Applications
The Applications (including but not limited to e-Anatomy and vet-Anatomy) each and individually are based on a set of instructions, programs, and rules. They are the expression of a unique source code created by the Editor.
Each of these Applications is an original software created by IMAIOS .
These Applications are more than the simple implementation of an automatic logic.
Each one has lines of programming, codes, a structure and language of development which are the reflection of creative choices and an intellectual contribution of the Editor.
The Applications are free and freely downloadable on the Android, Apple Store or other application platforms. However, some options are not free and the Editor reserves the right to charge for access to functions that are initially free, unilaterally and without notice.
2.2 Updating, interruption and availability of the Site and the Applications and their content
The Editor may, at any time, modify or delete information made available on the Site and/or any Application. It reserves the right to interrupt, temporarily or permanently suspend or modify access to all or part of the Site and the Applications, in order to ensure maintenance, or for any other reason, without this interruption giving rise to any obligation or compensation. Access to the Applications may also be interrupted or suspended due to unilateral decisions by Android or Apple Store.
Product and service specifications are subject to change without notice. Furthermore, IMAIOS does not guarantee that the products or services that are listed online or on the Applications will be available at the time of your order.
2.3 Scope
It is hereby expressly agreed that the granted access only allows the User to visit the Site and the Applications.
The User acknowledges that these Terms do not confer to the User any title of intellectual property rights (in particular as trademarks, designs or models) on the Site and the Applications.
3 SPECIFIC COMMITMENTS OF USERS
By using the Site and the Applications, the User agrees in particular not to:
- share his credentials with another user, each account being for strictly individual use;
- disrupt or interfere with the security of the Site and the Applications and their Content, resources (servers or networks connected to or accessible through the Site);
- disrupt or interfere with the enjoyment of any other User;
- upload, post or otherwise transmit through or on any site any virus or other harmful file;
- transmit through or on the Site or the Applications any type of unsolicited mass email to persons or entities who have not agreed to be part of such mailings;
- attempt to gain unauthorized access to the Site or the Applications or portions of the Site or the Applications that are restricted;
- use the Site or the Applications to seek, provide or obtain specific medical advice, medical opinion or diagnosis;
- use the Site or the Applications to seek, provide or obtain answers and/or specific lessons applied to a specific health-related examination.
4 QUALITY AND USE OF THE INFORMATION PROVIDED
4.1 Quality
The Editor endeavors to take the greatest care in the quality of the information provided on the Site and the Applications and in their regular updating. However, the Site and the Applications may contain erroneous or inaccurate information, omissions or data published independently of the Editor’s wish.
The Editor assumes no obligation to update the information available on the Site and the Applications.
The source of the data published on the Site and the Applications is explicitly mentioned with, if necessary, a hyperlink to this source. The date of the last modification appears clearly on the page of the Site or the Application concerned.
4.2 Usage
The Editor particularly draws the attention to the fact that the information published on the Site and on the Applications remains only indicative and for educational purposes without any express or tacit guarantee of any kind, for the exclusive use of health professionals duly authorized to practice in France, China or in their country of origin and health students, with the exception of the Applications which may be intended for a wider public.
This information shall in no way replace the opinion of health professionals or be considered or interpreted as advice or a recommendation of any kind.
The User shall not under any circumstances use the Site or the Applications to describe a condition, make a diagnosis, decide on a treatment or make any medical decision in the treatment of patients.
The User is in any case the only one responsible for the use of the information made available to him. He is invited to use it with discernment and to use his own professional judgment to evaluate it. The Editor further advises the systematic consultation of other sources of information.
5 AVAILABILITY OF PRODUCTS OR SERVICES
Any reference to an Editor product, application or service on the Site or the Applications does not imply that such product or service is or will be available in your country, where it may be subject to different regulations and conditions of use. This reference does not imply any intention on the part of the Editor to sell such product, application or service in the User's country. The Site and the Applications contain information on products and services that may or may not be available in all countries of the world. The User must ensure, prior to any use of the Site, the Applications or the products/services accessible via the Site and the Applications, that such use does not violate the laws of his country of residence.
The User is solely responsible for verifying whether the content of the Site, the Applications (or the products/services accessible from the Site or the Applications) complies with the legislation of the country from which he accesses the Site or the Application. The User is thus prohibited from using the Site or the Applications in a manner contrary to the legal, regulatory or ethical provisions applicable under the law of the country from which he accesses the Site or the Applications. The responsibility of the Editor or any other party involved in the creation and operation of the Site or the Applications shall not be engaged in case of non-compliance with the legislation of the country where the Site or the Applications are used.
6 LIABILITY AND WARRANTY
6.1 Exclusion of liability and warranty of the Editor
The Editor, its partners, its employees or any other party involved in the creation and operation of the Site and the Applications shall not be liable for any prejudice or damage, direct or indirect, of any nature whatsoever, resulting from the User’s access, use, even partial, or interpretation of the information on the Site or the Applications.
6.2 Liability and warranty of the User
The User guarantees and indemnifies the Editor, its partners, its employees or any other party involved in the creation and operation of the Site or the Applications against any action or claim from a third party due to the use of the Site or the Applications by the User or any harmful consequences directly or indirectly related to the use he makes of the Site or the Applications.
The User thus takes in charge the entirety of the damages to which the Editor, its partners, its employees or any other party implied in the creation and the exploitation of the Site and the Applications could be condemned as well as the legal expenses and the exposed fees.
6.3 Hyperlinks to third-party sites
The Site and the Applications are likely to contain hypertext links to other Internet sites managed by third parties. However, the Editor cannot proceed to the regular verification of the quality of these linked sites. The Editor cannot be held responsible for the content of these sites, nor for the services offered on these sites.
In addition, a summary and/or a link to a third party site does not imply that the Editor approves the site or the products or services on these third party sites. It does not guarantee the accuracy of any content referenced in such third party sites and will not be liable for any damages or injury resulting from access to or inability to access such sites.
7 OWNERSHIP OF THE SITE, APPLICATIONS AND THEIR CONTENT
7.1 Protection of the content of the Site and the Applications
All intellectual property rights on the Site, the Applications and their content (hereinafter "Content") including texts, databases, software, applications, slideshows, logos, images, drawings, graphics, animated sequences, sounds, videos are the property of the Editor or third parties having authorized the Editor to use them.
The whole of this Content is thus protected by the French and international legislations in particular on the copyright, the designs and models law, the trademark law, the database law.
The names and brands mentioned on the Site and the Applications are registered trademarks of the Editor or its beneficiaries.
It is explicitly agreed that the granted access to the Site and the Applications shall not be interpreted as a license granted to the User on the intellectual property rights held by the Editor. Therefore, any reproduction, imitation and more generally any exploitation of these trademarks are prohibited.
7.2 Use of the Site and the Applications - License granted
The Site and the Applications are intended exclusively for the personal and private use of the User.
The Editor grants the User a worldwide, non-exclusive, non-transferable, non-assignable, revocable license to use the Site and Applications for the duration of this Agreement and under the conditions set forth. The User acknowledges that the Site and Applications contain exclusive content, information, and materials that are protected by applicable intellectual property laws, in particular, copyright law. IMAIOS holds the intellectual property rights, including copyright, to the Site and Applications. The User acquires only a grant of rights, without any transfer of ownership.
The User is authorized to print or download the pages of the Site or print or take screenshots of the pages of the Applications under the following cumulative conditions:
- printing or downloading or, if applicable, printing or capturing, in a partial and reasonable manner (i.e. maximum 10% of the Site or the Application);
- no removal of any proprietary notices from the content, no modification of the content;
- use of printed, captured or downloaded information only for the personal and private use of the User, for non-commercial purposes;
- no public use, no distribution of printouts, captures or downloads.
Any other use (in particular any reproduction, representation, modification, adaptation, distribution for commercial purposes, lucrative or not) is strictly forbidden except prior express written agreement of the Editor.
The Editor being producer and owner of all or part of the databases present or used on the Site and the Applications, it is moreover strictly forbidden, for example, to extract and use all or part of the contents of the databases appearing on the Site and the Applications.
7.3 Hypertext links to the Site
It is not permitted to set up direct links to documents or pages within the Site, except with the prior authorization of the Editor.
All links to the Site must be approved in writing by IMAIOS, except in the following case:
- the link is a text link to the home page of the Site and not to pages of the Site;
- the link must display the homepage of the Site in full screen and not in a frame;
- the appearance, position, and other aspects of the link must not create the false impression that an entity or its activities or products are associated with the Editor.
In any event, the Editor reserves the right to withdraw its consent for a link without cause or notice, at any time.
8 Miscellaneous provisions
8.1 Duration
The Editor may terminate, modify, suspend or interrupt any access and use of the Site or the Application. He may remove, modify any content of the Site or the Application. It may impose limits on certain features and services or restrict access to all or part of the Site or the Application without notice or liability. The Editor reserves the right to terminate the authorization to use the Site, at any time and at its sole discretion.
8.2 Complaints
All complaints and reports of any abuse (for example, concerning a contentious contribution on the Site's discussion forums) or infringement of intellectual property rights must be made in writing to the contact address mentioned below.
In case of infringement of intellectual property rights, the following information must be provided:
- Identification, contact details and signature of the owner of the rights claimed to have been infringed;
- Mandate, if any, of the owner's representative for the purpose of issuing the notice of infringement;
- Precise description of the elements that do not respect the rights of the said owner and whose removal from the Site or an Application is requested;
- Declaration confirming the accuracy of the information transmitted to the Editor.
8.3 Breach of the User
The fact that the Editor does not take advantage of a breach by the User of any of the legal obligations or obligations referred to herein shall not be interpreted for the future as a waiver of the obligation in question and of the right to take advantage of this breach later.
If any provision of the Conditions is invalid under any law or any other rule of law, it shall be deemed unwritten, without invalidating the Conditions as a whole.
8.4 Applicable law and jurisdiction
The Site and the Applications are designed in France. They are hosted in the PRC. The Conditions are subject to the application of the PRC law. In the event of a dispute concerning the application or interpretation of the Conditions or, more generally, the use of the Site and the Applications by any individual or legal entity, it is expressly agreed that the courts in Jing’an District, Shanghai where the Editor is registered shall have sole jurisdiction, even in the event of multiple defendants or third-party claims.
8.5 Contact
IMAIOS (Shanghai) Information Consulting Co., Ltd. , Room 1578, Building 2, 1266 Nanjing West Road, Jing'an District, Shanghai, 200040, China Tel: +33 9 72 10 11 10
contact@imaios.cn
个人信息保护政策
Personal Information Protection Policy
本个人信息保护政策(本“政策”)于2025年6月20日更新并生效。
This personal information protection policy is updated and takes effect on June 20, 2025.
医脉欧(上海)信息咨询有限公司(定义见下文第1条,以下简称为“我们”或“IMAIOS”)深知个人信息对您的重要性,并会尽全力保护您的个人信息安全可靠。本政策介绍了我们如何收集、存储、使用、传输、对外提供您的个人信息以及您对您的个人信息所享有的各项权利及其实现路径。
IMAIOS (Shanghai) Information Consulting Co., Ltd. (see the definition in Article 1 below, hereinafter referred to as “We” or “IMAIOS”) know the importance of personal information to you and will try our best to ensure security of your personal information. This privacy policy introduces how we collect, store, use, transmit and provide your personal information externally as well as your rights to the personal information and the path to its realization.
本政策适用于医脉欧(上海)信息咨询有限公司的产品和服务,包括但不限于https://www.imaios.cn(以下简称“网站”)及应用程序e-Anatomy和vet-Anatomy(可在 Android、Apple Store 及其他平台上使用,以下简称“应用程序”)。本政策可能根据相关法律法规和IMAIOS的业务调整不时更新。因此,我们欢迎您关注我们不时公布的最新版本的政策,随时了解可能的更新。如果您对本政策有任何疑问、意见或建议,可根据本政策“联系我们”部分所列的联系方式与我们联络。
This Policy applies to the products and services of IMAIOS (Shanghai) Information Consulting Co., Ltd., including but not limited to, https://www.imaios.cn (the “Website”) and the mobile apps e-Anatomy and vet-Anatomy (available on Android, Apple Store and other platforms), Apple Store and other platforms, hereinafter referred to as “Apps”). This Policy may be updated from time to time in accordance with relevant laws and regulations and IMAIOS's business adjustments. Therefore, we welcome you to check the latest version of the Policy posted from time to time for possible updates. If you have any questions, comments or suggestions regarding this Policy, you may contact us at the contact information listed in the “Contact Us” section of this Policy.
1. 定义
Definition
“用户”:指同意本网站和应用程序的访问和使用条款的任何自然人或法人实体。
“User”: Any natural person or legal entity who agrees to the terms of access and use of the Website and the Application.
“服务”:由IMAIOS提供和操作的工具和/或平台和/或软件,包括任何IMAIOS通过网站、应用程序等向您提供的服务。
“Services”: the tools and/or platforms and/or software provided and operated by IMAIOS, including any IMAIOS services offered to you through the Website, APPs, etc. provided by IMAIOS to you.
“网站”: https://www.imaios.cn。
“Website”: https://www.imaios.cn.
应用程序:IMAIOS发布的e-Anatomy和vet-Anatomy等应用程序。
APP: Mobile applications such as e-Anatomy and vet-Anatomy published by IMAIOS.
“关联公司”:受控于IMAIOS、控制IMAIOS或与IMAIOS共同受同一实体控制的任何公司。控制指的是持有至少50%的股权或投票权。
“Associated company”: Any company that is controlled by, controls, or is under common control with IMAIOS by the same entity. Control is defined as holding at least 50% of the equity or voting rights.
“访客”:任何访问网站和应用程序的个人。
“Visitor”: Any individual who accesses the website and APP.
“个人信息”:以电子或者其他方式记录的与已识别或者可识别的自然人有关的各种信息,不包括匿名化处理后的信息。
“Personal information”: Various information related to identified or identifiable natural persons, recorded electronically or otherwise, other than anonymized information.
“个人信息处理者”:指在个人信息处理活动中自主决定处理目的、处理方式的组织。
“Personal information processor”: Refers to an organization that autonomously determines the purpose and manner of processing in personal information processing activities.
“匿名化处理”:指通过对个人信息的技术处理,使得个人无法被识别,且处理后的信息不能被复原的过程。个人信息经匿名化处理后所得的信息不属于个人信息。
“Anonymized processing”: Refer to the process in which personal information is processed technically to make individuals impossible to identify and the processed information can’t be recovered. The information obtained from anonymized processing doesn’t belong to personal information.
2. 本个人信息保护政策的适用范围
Scope of Application of this Personal Information Protection Policy
本政策适用于网站和/或应用程序以及您可能与IMAIOS进行的其他互动(例如,在线提交表单或电子邮件往来等)。
This policy applies to the website and/or APPs and other interactions you may have with IMAIOS (e.g., online form submissions or email exchanges, etc.).
请在使用我们的网站和/或应用程序或与我们进行其他互动前,仔细阅读并了解本政策,特别是以粗体标识的条款。如您选择使用或继续使用我们的服务和/或网站或与我们进行其他互动,即意味着您完全理解本政策的全部内容,并同意我们按照本政策处理您的相关信息。如果您不同意本政策的内容,请勿使用网站和/或应用程序,并停止与IMAIOS的任何互动。
Please read and understand this Policy, especially the terms identified in bold, carefully before using our websites and/or APPs or otherwise interacting with us. By choosing to use or continue to use our Services and/or Website or otherwise interact with us, you are implying that you fully understand this Policy in its entirety and that you consent to our processing of information about you in accordance with this Policy. If you do not agree with the contents of this Policy, please do not use the Website and/or the APP and cease any interaction with IMAIOS.
本政策不适用于您通过网站和/或应用程序或者与我们的其他互动使用第三方提供的服务,请您在使用所有第三方的服务前了解相关第三方的政策,我们在服务、网站或者与您的其他互动中使用第三方的服务,并不表示我们认同第三方的政策或为第三方的个人信息处理活动提供任何保证。
This Policy does not apply to your use of services provided by third parties through the Websites and/or APPs or other interactions with us, please be aware of the relevant third party's policies before using all third party's services, and our use of a third party's services in connection with the Services, the Websites, or in other interactions with you does not imply that we subscribe to the third party's policies or provide any warranty for the third party's personal information processing activities.
3. 我们如何收集和使用您的个人信息
How we collect and use your personal information
我们的网站和应用程序免费开放并可自由访问和下载,通常无需创建客户账户,但某些服务的实现除外。作为个人信息处理者,我们通过以下方式收集个人信息:
Our website and APPs are free, open, and freely accessible, and downloadable, and do not typically require the creation of a customer account, except to enable certain services. As a personal information processor, we collect personal information through the following means:
● 当您通过创建或更新帐户、订阅服务、填写表格或通过支持或反馈渠道与我们联系而自愿提供信息时;
When you voluntarily provide information by creating or updating an account, subscribing to services, completing forms, or contacting us through support or feedback channels;
● 当您使用我们服务的过程中需要身份验证或个性化的特定功能时(访问高级资源);
When you use specific features of our services that require authentication or personalization (accessing premium resources);
● 通过自动化手段(包括cookies和类似的跟踪技术)收集,以帮助我们改进服务功能,分析使用模式,增强用户体验;
Through automated means, including cookies and similar tracking technologies, which help us improve service functionality, analyze usage patterns, and enhance user experience;
● 当您启用并授权集成时,通过您连接的第三方服务或平台收集。
From third-party services or platforms you connect with, when such integration is enabled and authorized by you.
这些个人信息是根据适用的法律收集的,并且仅出于本政策中明确声明的目的。
This personal information is collected in accordance with applicable laws and solely for the purposes explicitly stated in this Policy.
(1)由IMAIOS的用户主动提供的个人信息
Personal information voluntarily provided by IMAIOS users
当您订阅或使用IMAIOS服务时(包括但不限于:创建用户账户以访问服务;IMAIOS为用户提供与服务相关的支持时);或者当您订阅时讯简报、参与IMAIOS组织的各种活动(包括营销活动、讨论组、比赛、满意度调查、网络研讨会等)或与IMAIOS的社交网络账户进行互动或以其他方式与IMAIOS交流时;或者当您通过网站、应用程序等渠道上公布的联系方式,以电子邮件或任何其他方式联系我们,尤其是为了获取有关IMAIOS产品或服务的信息时,我们将收集您提供的姓名、电话号码、电子邮箱、地址、职业、机构或公司,您理解此类信息是为向您提供相应的资讯信息或服务所必需。如您拒绝提供您的上述信息,我们可能无法向您提供您需要的相关资讯信息或服务并与您有效互动,但不影响您使用IMAIOS向您提供的其他服务或与IMAIOS进行其他互动。
When you subscribe to or use the IMAIOS Services (including, without limitation, when you create a user account to access the Services; when IMAIOS provides support to its users in connection with the Services); or when you subscribe to newsletter bulletins, participate in events organized by IMAIOS (including marketing campaigns, discussion groups, contests, satisfaction surveys, webinars, etc.) or interact or otherwise communicate with IMAIOS' social network accounts; or when you contact us by email or any other means through the contact information published on the Website and other channels, in particular in order to obtain information about IMAIOS' products or services. when you interact or otherwise communicate with IMAIOS; or when you contact us by e-mail or any other means through the contact information published on the website, application, etc., in particular in order to obtain information about IMAIOS' products or services, we collect the name, telephone number, e-mail address, address, occupation, organization or company that you provide, and you understand that such information is used in order to provide you with You understand that such information is necessary to provide you with appropriate information or services. If you refuse to provide your information as described above, we may not be able to provide you with the relevant information or services that you need to interact effectively with us, but this will not affect your ability to use other services offered to you by IMAIOS or to interact with IMAIOS.
(2)在您使用网站及/或服务过程中记录的个人信息
Personal information recorded in the course of your use of the Website and/or the Services
当您访问我们的网站和使用我们的服务时,为了维护我们网站、服务的正常运行,改进及优化我们的网站、服务体验以及保障网络操作环境安全或基于遵守法律法规规定的需求,我们会自动收集一些个人信息:
When you visit our website and use our services, in order to maintain the normal operation of our website and services, improve and optimize the experience of our website and services, as well as to ensure the safety of the network operating environment or based on the need to comply with the provisions of laws and regulations, we will automatically collect some personal information.
● 元数据:元数据是指描述数据的数据,主要是描述数据属性的信息,用来支持如【指示存储位置、历史数据、资源查找、文件记录…】等功能。当用户访问服务时,系统会生成元数据以提供有关用户工作方式的额外信息,并方便访问和使用我们提供的功能。
Metadata: Metadata is the data that describes the data, mainly information that describes the attributes of the data and is used to support features such as historical data, resource lookups, file logging and so on. When a user accesses the service, the system generates metadata to provide additional information about how the user works and to facilitate access to and use of the features we provide.
● 连接和使用数据:当您访问网站和通过互联网使用服务时,IMAIOS的服务器会自动收集和存储信息。这些信息包括您的Internet协议地址(IP地址)、您在使用网站或服务之前访问的网页地址、您使用的浏览器类型及其配置和插件信息、您使用服务的日期和时间、您的语言首选项和cookie数据 (更多详细信息,请参考我们的cookie政策,见附件1)。
Connection and Usage Data: IMAIOS servers automatically collect and store information when you visit the Site and use the Services over the Internet. This information includes your Internet Protocol address (IP address), the address of the web page you visited before using the Website or the Services, the type of browser you are using and its configuration and plug-in information, the date and time you use the Services, your language preference and cookie data (for more detailed information, please refer to our cookie policy, see Appendix 1).
● 设备数据:IMAIOS将收集设备数据,包括设备类型、操作系统、设备设置、应用程序ID、唯一设备ID和停机数据,以便您下次访问网站或使用服务时更加轻松便捷。
Device Data: IMAIOS will collect device data, including device type, operating system, device settings, application ID, unique device ID, and downtime data, to make your next visit to the Site or use of the Services easier and more convenient.
● Cookie:IMAIOS将通过网站和服务上的cookie和类似技术收集数据。网站和服务中可能还包括cookie和类似的追踪技术,这些技术可能会通过第三方服务收集您的数据。如需了解更多有关IMAIOS如何使用这些技术的信息,请参考我们的cookie政策,见附件1。
Cookie: IMAIOS will collect data through cookies and similar technologies on the Sites and Services. The Sites and Services may also include cookies and similar tracking technologies that may collect data about you through third party services. For more information on how IMAIOS uses these technologies, please refer to our cookie policy, see Annex 1.
● 软件开发包(SDK)和应用程序接口 (API) 等代码:IMAIOS将通过接入由第三方提供的软件开发包(SDK)、应用程序接口 (API) 等代码或通过其他合作方式,以保障相关功能的实现与应用安全稳定的运行。请参考我们的SDK和API清单,见附件1。第三方合作方具体的数据处理情况请参见其隐私政策或相关服务说明。请注意,第三方合作方的代码可能因为其版本升级、策略调整等原因导致数据处理类型存在一定变化请以其公示的官方说明为准。
Software development kits (SDKs) and application programming interfaces (APIs) and other codes: IMAIOS will integrate software development kits (SDKS), application programming interfaces (APIs) and other codes provided by third parties or through other cooperative methods to ensure the realization of related functions and the safe and stable operation of applications. Please refer to our SDK and API list, see Annex 1. For specific data processing details of the third-party partners, please refer to their privacy policy or relevant service descriptions. Please note that the third-party partners’ code may have certain changes in data processing types due to version upgrades, policy adjustments, etc. Please refer to their official explanations.
(3)来自其他来源的个人信息
Personal information from other sources
我们也可能通过以下方式进行收集您的个人信息:
We may collect your personal information by the following ways:
第三方数据:IMAIOS可能会从其关联公司、合作伙伴或IMAIOS用于提高数据质量和相关性的其他方处接收您的个人信息,如身份识别数据或专业数据。此类数据也可以是更精确的数据,例如用于分析在线营销活动、满意度调查、招聘或电子邮件营销活动绩效的数据。我们在收集上述信息前将依法采取合理措施确保这些第三方提供给我们的个人信息符合法律的规定。
Third-party data: IMAIOS may receive your personal information such as identity data or professional data from its associated company, partners or other parties that IMAIOS uses to improve the data quality and relevance. Such data can also be more accurate data, such as the data used for analyzing online marketing campaign, satisfaction survey, recruitment or email marketing campaign performance. Before collecting above information, we will take reasonable measures to ensure the personal information provided to us by these third parties conforms to the laws.
4. 我们保存您个人信息的期限
The period for retaining your personal information
IMAIOS作为个人信息处理者,仅为实现服务目的所必需的时间存储您的个人信息(详情见下表)。当我们的服务或网站发生停止运营的情形时,我们将依照法律的规定以公告、邮件通知等形式通知您,在合理的期限内删除您的个人信息或进行匿名化处理,并立即停止收集个人信息的活动,以及关闭第三方应用服务接口,避免第三方通过服务继续收集您的个人信息。
As personal information processor, IMAIOS can only retain your personal information for the period required to achieve the service purpose (see details as below). When our Service or Website stops operation, we will notify you in the form of public announcement or email according to provisions of the law and delete your personal information or conduct anonymization within a reasonable period and stop collecting personal information and close the third-party application service interface to prevent third party from collecting your personal information through the Service.
我们网站和应用程序上收集的数据和个人信息将由我们的托管服务提供商 AWS 中国(宁夏)区域托管,由宁夏西云数据科技有限公司(NWCD)运营。
Data and personal information collected on our website and applications will be hosted by our hosting service provider, AWS China (Ningxia), and operated by Ningxia Xiyun Data Technology Co., Ltd. (NWCD).
服务目的 Purpose of Service | 期限 Term |
用于管理客户账户和其他行政任务,例如开具发票 For managing customer accounts and other administrative tasks, such as invoicing | 合同期限和法定保留期 Contract Term and Statutory Retention Period |
用于市场营销(营销活动、在线活动或贸易展会、客户满意度调查) Marketing (marketing events, online events or trade shows, customer satisfaction surveys) | 撤回同意时或注销账户时 Withdrawal of consent or cancellation of account |
进行安全调查,帮助防止安全或欺诈问题,以及潜在的滥用 Conduct security investigations to help prevent security or fraud issues, as well as potential abuse | 进行安全或欺诈调查及其解决所需的时间。如发生诉讼,可能延长 Time needed for security or fraud investigation and its resolution. This may be extended in case of litigation. |
管理通过联系表格或任何其他方式提出的请求 Manage requests via contact form or any other means | 撤回同意或处理请求 Withdrawal of consent or processing request |
网站访客的统计数据和报告 Statistics and Reports of Site Visitors | 不同保留期(请参考我们的Cookie政策) Different retention periods (please refer to our cookie policy) |
5. 我们如何向第三方共享和披露您的个人信息
How we share and disclose your personal information to third parties
在以下情况下,我们将另行通知并征求您的同意:(i) 向其他个人信息处理者提供您的个人信息,(ii) 公开您的个人信息,(iii) 处理敏感个人信息,(iv) 向境外提供个人信息,除非适用法律另有允许。我们将根据具体情况向您进行披露。我们承诺仅共享为了实现共享目的所必要的您的个人信息,且我们的共享仍受本政策的约束;如果我们要改变个人信息的使用及处理目的,我们将确保在遵守所有适用的法律依据后再进行此类变更。
We will provide further notice and seek your consent to (i) provide your Personal Information to other processors of Personal Information, (ii) disclose your Personal Information, (iii) process sensitive Personal Information, and (iv) provide Personal Information outside of the country, unless otherwise permitted by applicable law. We will make disclosures to you on a case-by-case basis. We are committed to sharing only as much of your Personal Information as is necessary to fulfill the purposes for which it was shared, and our sharing remains subject to this Policy; if we change the purposes for which the Personal Information is used and processed, we will ensure that we comply with all applicable legal authorities before making such changes.
请知悉,我们收集的数据由托管服务提供商 AWS 中国(宁夏)区域托管,由宁夏西云数据科技有限公司(NWCD)运营。
In particular, please be aware that the collected data is hosted by our hosting provider, AWS China (Ningxia) Region, operated by Ningxia West Cloud Data Technology Company Limited (NWCD).
在此背景下,我们自然遵守现行数据保护法律:我们与托管服务提供商的合作需遵守标准合同条款(您通过接受本政策确认此项内容),这些条款要求其确保高水平的数据安全,以防止未经授权的第三方欺诈性访问以及任何未经授权的数据破坏、更改或分发。
In this context, we naturally comply with current data protection laws: our cooperation with hosting service providers is subject to standard contractual clauses (which you acknowledge by accepting this policy), which require them to ensure a high level of data security to prevent fraudulent access by unauthorized third parties as well as any unauthorized destruction, alteration or distribution of data.
6. 我们如何保护您的个人信息
How we protect your personal information
IMAIOS关注您个人信息的安全。因此,IMAIOS采取了技术和组织措施来保证您个人信息的安全,并防止任何丢失或误用的风险以及任何未经授权的访问或披露。这些措施充分考量了IMAIOS收集、处理和存储的信息的敏感性以及技术水平。
IMAIOS is concerned about the security of your personal information. Therefore, IMAIOS has taken technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of your personal information and to prevent any risk of loss or misuse as well as any unauthorized access or disclosure. These measures take full account of the sensitivity of the information collected, processed and stored by IMAIOS, as well as the level of technology.
6.1技术安全措施
Technical security measures
(1) 个人信息加密:根据具体的处理活动和个人信息的敏感程度,IMAIOS作为个人信息处理者,在存储和传输个人信息(静态)时使用个人信息加密技术措施。
Encryption of personal information: Depending on the specific processing activities and the sensitivity of the personal information, IMAIOS, as a processor of personal information, uses technical measures for encryption of personal information when storing and transmitting personal information (at rest).
(2) IMAIOS(或委托的高安全标准的第三方托管提供商)将采取必要技术措施确保处理系统和服务的持续机密性、完整性、可用性和恢复能力。
IMAIOS (or a commissioned third party hosting provider with high security standards) will take the necessary technical measures to ensure the continued confidentiality, integrity, availability and resilience of processing systems and services.
(3) 在发生物理或技术事故时,我们将启动预案,及时恢复个人信息可用性和访问的能力,阻止事故扩大,并依法履行相应的报告及通知义务。
In the event of a physical or technical incident, we will activate a plan to restore the availability of and access to personal information in a timely manner, prevent the incident from expanding, and fulfill the appropriate reporting and notification obligations in accordance with the law.
(4) IMAIOS(或独立外部机构)将定期测试、评估和评价内部信息系统,确保数据处理安全的技术和组织措施的有效性,该系统可能包含个人数据。由独立外部机构定期进行的其他测试有助于检查现有技术和组织措施的功效,从而在发现薄弱环节的后即使制定专门的补救计划。
IMAIOS (or an independent external body) will periodically test, assess and evaluate the effectiveness of technical and organizational measures to ensure the security of internal information systems, which may contain personal data. Other tests conducted periodically by an independent external body will help to check the effectiveness of existing technical and organizational measures so that specific remediation plans can be put in place as soon as weaknesses are identified.
6.2组织安全措施
Organization security measures
(1) 信息安全政策:无论是对于我们的内部流程还是对于我们的用户而言,信息安全都是我们公司的支柱。因此,根据业务要求和现行法律法规,我们建立专门的管理制度、流程和组织以保障信息安全。
Information Security Policy: Information security is the backbone of our company, both for our internal processes and for our users. Therefore, in accordance with business requirements and current laws and regulations, we have established special management systems, processes and organizations to safeguard information security.
(2) 信息安全组织:建立、记录和监控组织管理框架,以启动并验证组织内信息安全的实施和运行。
Information Security Organization: establishes, documents, and monitors the organizational management framework to initiate and validate the implementation and operation of information security within the organization.
(3) 人力资源管理安全:员工和承包商均理解其职责。所有员工和承包商在履行其职责时均须遵守保密条款。此外,应定期实施信息安全意识计划和个人信息处理优良实践,确保员工和承包商能够了解其职责和相关重大问题。
Human resources management security: Employees and contractors understand their responsibilities. All employees and contractors are subject to confidentiality clauses in the performance of their duties. In addition, information security awareness programs and good practices for handling personal information should be implemented regularly to ensure that employees and contractors are aware of their responsibilities and the significant issues involved.
互联网并非绝对安全的环境,而且电子邮件、即时通讯、社交软件等与其他用户的交流方式无法确定是否完全加密,我们建议您在使用此类工具时设置复杂密码,并注意保护您的个人信息安全。
The Internet is not an absolutely secure environment, and there is no way to be sure that email, instant messaging, social software and other methods of communicating with other users are fully encrypted, so we recommend that you set up complex passwords when using such tools and take care to protect the security of your personal information.
7. 您的个人信息如何跨境传输
How your personal information is cross border transferred
由于IMAIOS是一家跨国公司,基于集团运营和管理的需要(例如提高管理效率、客户满意度以及风险管理),我们通过遍布全球的资源和服务器提供产品或服务,这意味着,IMAIOS可能会将您的个人信息传输到您所在国家/地区以外的其他国家/地区,或者您的个人信息受到来自您所在国家/地区以外的其他国家/地区的访问。我们将遵守中国法律规定,利用便捷安全的国际数据传送工具,在确保保护措施充分安全的前提下传输您的个人信息,并且始终保持您的个人信息安全可控。IMAIOS将确保您的个人信息得到在中华人民共和国境内足够同等的保护。我们将始终在管理、技术处理等过程确保信息安全,防止您的个人信息受到各种可预见事故的危害。您承认并同意,我们可以为本政策所述之目的,根据本节所述之条款和条件,与关联公司和/或我们的合作伙伴共享您的个人信息。
Because IMAIOS is a multinational company, we provide products or services through resources and servers around the world based on the needs of the group's operations and management (e.g., to improve management efficiency, customer satisfaction, and risk management), which means that IMAIOS may transfer your personal information to countries other than the country in which you are located or your personal information may be subject to access from countries other than the country in which you are located, or from countries other than the country in which you are located. country/region other than the one in which you are located. We will comply with Chinese laws and regulations, utilize convenient and secure international data transfer tools, transfer your personal information in a manner that ensures adequate protection and security, and maintain control over the security of your personal information at all times. IMAIOS will ensure that your personal information receives the same level of protection as it would receive if it were in the People's Republic of China. We will at all times ensure the security of information in our management, technical processing and other processes to prevent your personal information from being jeopardized by any foreseeable incident. You acknowledge and agree that we may share your personal information with our affiliates and/or our partners for the purposes described in this Policy and in accordance with the terms and conditions described in this section.
跨境数据传输同意通知请见附件2。
Cross-Border Data Transfer Consent Notice is listed in Appendix 2.
8. 未成年人保护
Protection of minors
IMAIOS不对未满18周岁的未成年人提供服务,也不会主动向未成年人寻求或收集个人信息。请您在使用我们的服务前,确保自己是有完全民事权利能力和行为能力的成年人。如果我们发现自己在未事先获得可证实的父母或其他监护人同意的情况下收集了未成年人的个人信息,我们会设法尽快删除相关信息。
IMAIOS does not provide services to minors under the age of 18 and does not actively seek or collect personal information from minors. Please ensure that you are an adult with full civil rights and capacity to act before using our services. If we discover that we have collected personal information from a minor without first obtaining verifiable parental or other guardian consent, we will attempt to delete the information as quickly as possible.
9. 用户和访客的权利
Rights of Users and Visitors
用户和访客有权要求访问其个人信息,以及复制、更新、删除、更正和转移其个人信息,并在法定情况下,有权撤回其同意,反对或限制对其个人信息的处理。我们将采取适当的技术和管理手段,保证您的上述权利得以实现。您的权利包括:
Users and visitors have the right to request access to their personal information, as well as to copy, update, delete, correct and transfer their personal information and, in the statutory cases, to withdraw their consent and to oppose or limit the processing of their personal information. We will take appropriate technical and administrative measures to ensure that your rights mentioned above are realized. Your rights include:
● 查阅权和复制权。查阅我们持有的您的个人信息,并要求提供个人信息的副本。
Right of access and reproduction: review your personal information that we hold and request for a copy of personal information.
● 更正权。如果您的个人信息不准确或不完整,要求我们更新或更正。
Correction rights: If your personal information is inaccurate and incomplete, request us to update or correct it.
● 删除权。如果您不再使用我们的产品或服务,或在其他法定情况下,要求我们删除您的个人信息,除非我们有法律或法规义务保留该信息。
The right of deletion: If you don’t use our products or services or in other statutory circumstances, you can request us to delete your personal information, unless we have legal or regulatory obligation to retain this information.
● 撤回同意权。在我们收集您的信息是基于知情同意的合法性基础上,您可以反对或撤回您对我们处理您个人信息的同意。
The right to withdraw consent: We collect your information based on the legality of informed consent. You can oppose or withdraw your consent to our processing of your personal information.
● 注销账户权。在满足法律规定的情况下,您可以要求我们注销您的账户;若您是组织内的用户,前提是您的组织同意。
The right of canceling account: You may request us to cancel your account on the premise of meeting the legal provisions. If you are a User within an Customer’s organization, you shall get the consent of your organization first.
● 可携带权。在符合监管部门规定的要求下,您可以指示我们将您的个人信息转移给您指定的另一个个人信息处理者。
Right of portability: You can instruct us to transfer your personal information to another personal information processor designated by you, provided that the requirements of the regulatory authorities are met.
当您通过本网站或其他任意方式向我们提供您的个人信息时,无论您作为用户或是访问者, 您可通过如下第11条“联系我们”行使您的相关权利。
When you provide your personal information to us through this Website, or any other mean, either you are a User or a Visitor, you can exercise above rights by using the contact described in Section 11 below “Contact US”.
除以上的个人信息权利行使的具体方式之外,您还可以通过“联系我们”中列明的方式联系我们,我们将在15个工作日内回复您的请求。特别提醒,收到您的特定请求(包括访问、更正、删除个人信息和注销账户、转移个人信息)后,我们可能会首先验证您的身份,在验证通过的情况下才会响应您的请求。另外,如果您的请求特别复杂或您提出了许多请求,我们可能需要超过15个工作日的时间处理。在这种情况下,我们会及时通知您并向您通报最新情况。
In addition to the above specific ways to exercise your rights with respect to your Personal Information, you may contact us in the manner set forth in ‘Contacting US’ and we will respond to your request within 15 business days. In particular, upon receipt of your specific request (including access, correction, deletion of personal information and cancellation of accounts, transfer of personal information), we may first verify your identity and will respond to your request only if we are able to do so. Additionally, if your request is particularly complex or you make many requests, it may take us more than 15 business days to process. In such cases, we will notify you and keep you updated.
如果您想访问、更正、删除您的组织委托我们存储的客户内容,您可以:(1)在您获得的授权范围内自行行使上述权利;或(2)在超越授权范围时通过联系您的组织获得必要帮助来行使您的权利。
If you wish to access, correct, or delete Customer Content that your organisation has entrusted to us for storage, you may either (1) exercise the above rights yourself within the scope of the authorisation you have been granted, or (2) exercise your rights by contacting your organisation to obtain the necessary assistance in the event that the scope of the authorisation is exceeded.
10. 本个人信息保护政策如何更新
How we update this privacy policy
我们可能会不定时修改本政策,以便及时反映法律法规的变化以及我们服务政策的调整。在我们修改本政策后,您继续使用我们的服务将视为您对本政策相关调整的同意。
We may change this Privacy Policy from time to time to reflect changes in laws and regulations as well as changes in our service policies. After we amend this privacy policy, your continuous use of our Services will be deemed as your consent to the changes in this privacy policy.
未经您明确同意,我们不会削减您按照本政策所应享有的权利。对于重大变更,我们还会提供更为显著的通知(包括对于某些服务,我们会通过电子邮件发送通知,说明政策的具体变更内容)。
We will not diminish your entitlement under this Policy without your express consent. For major changes, we will provide more significant notice (e.g. for some services, we will send notice via e-mail about specific changes to our privacy policy) .
本政策所指的重大变更包括但不限于:
Significant changes to this policy include but not limited to:
(1) 我们的服务模式发生重大变化。如处理个人信息的目的、处理的个人信息类型、个人信息的使用方式等;
Significant changes in our service mode: e.g. the purpose of personal information processing, the type of personal information processing, the way in which personal information is used, etc;
(2) 我们在所有权结构、组织架构等方面发生重大变化。如业务调整、破产并购等引起的所有者变更等;
Major changes in ownership structure, organizational structure, etc; such as change of owner caused by business adjustment, bankruptcy merger and acquisition, etc;
(3) 个人信息共享、转让或公开披露的主要对象发生变化;
Changes in the main objects of personal information sharing, transfer or public disclosure;
(4) 您参与个人信息处理方面的权利及其行使方式发生重大变化;
Significant change in your right to participate in processing personal information and in the manner in which the right is exercised;
(5) 我们负责处理个人信息安全的责任部门、联络方式及投诉渠道发生变化时;
Changes occur in the department responsible for handling personal information security, contact information and complaint channels;
(6) 个人信息安全影响评估报告表明存在高风险时。
The personal information security impact assessment report indicates that a high risk exists.
11. 联系我们
Contact US
任何人均可就本政策或IMAIOS的个人信息实践或为行使其权利而联系IMAIOS。如果您希望联系IMAIOS,请发送邮件至contact@imaios.cn,或写信至以下地址:
Anyone may contact IMAIOS concerning this Policy or the IMAIOS Personal Information practices, or to exercise their rights. Should you wish to contact IMAIOS, please send an e-mail to contact@imaios.cn, or write to the following address:
Denis HOA 先生,上海市静安区南京西路1266 号2幢1578室,邮编:200040.
Mr. Denis HOA, Room 1578, Building 2, No. 1266 Nanjing West Road, Jing 'an District, Shanghai 200040.
我们将尽快审核所涉问题,并在接到咨询、投诉之日起15个工作日内予以回复。
We will examine and verify the issues in question as soon as possible and respond to the inquiries and complaints within 15 working days from the date of receipt.
APPENDIX 1 Cookie Policy & SDK and API List
Cookie Policy
Cookie是一种字符串信息形式的小型数据文件,通过本网站 的互联网服务器发送至你的设备硬件上的特定位置。你的浏览器将储存这个Cookie,当你再次登录时,浏览器会把Cookie发送给网站的服务器。Cookie根据适用法律和你的选择被存放并储存在你的设备上,你可以在下述条件下随时进行更改。
A cookie is a small data file in the form of a string message that is sent to a specific location on your device's hardware by the Web site's Internet server. Your browser will store this cookie and send it to the Web site's server when you log in again. Cookies are subject to applicable law.
Cookie有几种用:记住你的登录信息,便于你能快速登录你的账户,为了统计目的,跟踪你的会话和浏览活动,或识别你感兴趣的话题,以便为你提供相关内容。
Cookies are used for several purposes: to remember your login information so you can quickly log in to your account, for statistical purposes, to track your conversations and browsing activity, or to identify topics of interest so you can be served relevant content.
Cookie文件允许其发布者识别其储存的设备,并在Cookie的有效期或储存期内,收集设备上的浏览信息。
A cookie file permits its publisher to identify the device on which the cookie is stored and to collect browsing information from that device for the duration of the cookie's validity or storage period.
会话COOKIES
SESSION COOKIES
这些Cookies不能用于收集用户或其活动的信息,也不能用于收集用于市场营销或确定目标相关的任何信息,但它们可用于对网站访问量进行全面的统计监测。
These cookies should not be used to gather information about the users or their activity and should not be used to collect any information for marketing or targeting use, but they can be used to provide overall statistical monitoring of traffic to the Site.
分析型Cookies
Analytical cookies
这些Cookies有助于我们生成统计数据,帮助我们优化内容和网站。这些统计数据是作为聚合数据生成的,而非个人数据。当用户退出网站时,分析型Cookies不会自动删除。这类cookies只有在用户接受它们时才能保存。
These cookies help us generate statistics that help us optimize our content and Web site. These statistics are generated as aggregate data, not individual data. Analytic cookies are not automatically deleted when a user leaves the Web site. These cookies persist only if the user accepts them.
第一方Cookies
First Party Cookies
此类Cookies由网站设置者直接放置于您的设备并仅能由我们的服务读取。
These cookies are placed directly on your device by the website setter and can only be read by our services.
第三方Cookies
Third Party Cookies
这些Cookies有助于用户使用第三方网站提供的服务。它们也可以向用户提供其感兴趣的内容。这类cookies只有在用户接受它们时才能保存。
These cookies help users use services provided by third-party Web sites. They can also provide users with content that they are interested in. These cookies persist only if the user accepts them.
https://www.imaios.cn网站上的cookies描述如下:
The cookies on the https://www.imaios.cn website are described as follows:
序号 Serial number | Cookie类型 Cookie Types | Cookie名称 Cookie Name | Cookie功能 Cookie Functionality | 发布Cookie的网站 Website that issues cookies | 存储期限 Storage period |
1 | JWT | auth | 访问权限管理 Rights management for application accessibility
| imaios.cn | 5分钟 5 minutes
|
2 | 哈希字符串 Hashed string
| eZSESSID_dxp_imaios | 用户联系 User connexion
| imaios.cn | 60天 60 days
|
接受COOKIES的使用
Acceptance of Cookies
我们使用cookies以确保网站能良好运作,并且通过收集有关用户设备(例如:设备及浏览器)及个人喜好的信息,方便用户浏览网站。因此,如果你想要以一种全面优化的方式使用本网站,我们建议你接受这些Cookies。你可以点击此处,随时更改Cookie的设置,例如:撤回你的同意。如果你撤回你的同意,我们将停止在本网站上收集你的cookies。
We use cookies to ensure that the website works well and to facilitate browsing by collecting information about the user's equipment (e.g. device and browser) and personal preferences. Therefore, if you want to use this website in a fully optimized way, we recommend that you accept these cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time, for example, by withdrawing your consent, by clicking here. If you withdraw your consent, we will stop collecting your cookies on this website.
此外,你可以根据以下链接的提示,设置你的浏览器以修改Cookie设置。
In addition, you can set your browser to modify cookie settings according to the instructions in the following link.
- 对于Internet Explorer浏览器:
- For Internet Explorer browser:
- 对于Safari
- For Safari
https://support.apple.com/zh-cn/HT201265;
- 对于Chrome
- For Chrome
https://support.google.com/chrome/answer/95647?hl=zh-Hans;
- 对于Firefox
- For Firefox
或与我们联系,我们将指导您如何修改Cookie设置。
Or contact us and we will guide you how to modify your cookie settings.
对Cookie政策的更新
Updates to our Cookie Policy
我们可能会时不时更新本Cookie政策。我们建议您不时查看本政策,以便及时了解我们如何使用cookies。本Cookie政策最后一次更新于2025年6 月20 日。
We may update this Cookie Policy from time to time. We recommend that you check this policy from time to time to keep up to date with how we use cookies. This Cookie Policy was last updated on 20 June 2025.
SDK and API List
为保障IMAIOS 的应用程序相关功能的实现与应用安全稳定的运行,我们可能会接入由第三方及关联方提供的软件开发包(SDK)、应用程序接口 (API) 等代码或通过其他合作方式,以实现相关目的。我们会对获取信息的合作方的代码进行严格的安全监测,以保护数据安全。第三方合作方具体的数据处理情况请参见其隐私政策或相关服务说明。请注意,第三方合作方的代码可能因为其版本升级、策略调整等原因导致数据处理类型存在一定变化请以其公示的官方说明为准。
To ensure the functionality, security, and stable operation of the IMAIOS APPs, we may integrate third-party or their affiliates’ Software Development Kits (SDKs), Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), or other codes through cooperative partnerships to achieve relevant objectives. We will monitor the security of the codes provided by our partners to safeguard data security. For details on how our third-party partners process data, please refer to their respective privacy policies or related service descriptions. Please note that the data processing practices of these third-party partners may change due to version updates, policy adjustments, or other reasons. Please refer to their officially published documentation for the most accurate information.
微信分享&登录&支付SDK
WeChat Sharing, Login & Payment SDK
- 厂商:腾讯科技(深圳)有限公司
Provider: Tencent Technology (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd.
- 合作目的:微信分享&登录&支付
Purpose: WeChat sharing, login, and payment
- 收集个人信息类型:设备地址、Android ID、设备型号、手机号码
Types of Personal Information Collected: Device address, Android ID, device model, cellphone number
- SDK隐私政策链接:
SDK Privacy Policy Link:
https://support.weixin.qq.com/cgi-bin/mmsupportacctnodeweb-bin/pages/RYiYJkLOrQwu0nb8
附件2 跨境数据传输同意通知
APPENDIX 2 Cross-Border Data Transfer Consent Notice
跨境数据传输同意通知
Cross-Border Data Transfer Consent Notice
请仔细阅读并确认同意。
Please read carefully and check to agree.
1. 数据传输
1. Data Transfer
您的下列个人信息将按以下方式传输:
Your personal information listed below will be transferred as follows:
海外数据接收者及其联系信息 Overseas data recipients and their contact information | 业务场景和处理目的 Business Scenarios and processing purposes | 海外接收方处理的个人信息类别 Categories of personal information to be processed by the overseas recipient |
IMAIOS contact@imaios.com | 用于用户对应用程序提供反馈的弹窗 Popup dedicated to user feedbacks on the application | 用户电子邮箱,来自用户的消息(自由文本字段)。 Email of the user, message from the user (free text field).
应用名称、应用版本、是否为playstore版本(否)、解剖结构代码语言、设备android版本、imaios MUID(应用安装时的唯一id)、网名、订阅状态(会员;是否有订购到期日,是否作为机构用户注册;或未注册) App name, app version, Is the playstore version (no), code language of anatomical structures, android version of the device, imaios MUID (unique id by app installation), Screen name, Subsciption status (Member; or Subscribed with expiration date & institution or not; or unregistered ) |
支付信息元数据 Payments information metadata | UID -用户唯一标识符 UID - Unique identifier by user | |
IMASTAT使用统计IMASTAT usage statistics | session_id IP地址/IP address 用户代理/User agent 移动用户识别号/MUID | |
提供支持和服务改进 For support and service improvement | 姓名/Name UID电子邮箱/Email 登录(识别符)/Login (identifier) IP地址/IP address 收件地址/Postal address |
我们使用加密和合同保障措施来保护您的数据。
We use encryption and contractual safeguards to protect your data.
我们充分理解个人信息的重要性,因此我们将确保海外接收方严格遵守当地的个人信息保护法,并确保所有处理活动均达到中华人民共和国相关法律法规规定的个人信息保护标准,以确保您的个人信息得到充分保护。
We fully understand how important the personal information is, so we will ensure that the overseas recipient strictly observes the local personal information protection law and that all the processing activities are up to the personal information protection standards stipulated by the relevant laws and regulations of the People's Republic of China, so as to ensure that your personal information is adequately protected.
2. 您的权利
2. Your Rights
撤销同意(可能影响服务)
Withdraw consent (may affect service)
访问或要求删除
Access or request deletion
联系我们 医脉欧(上海)信息咨询有限公司 contact@imaios.cn/+86-13788973207
Contact us: IMAIOS (Shanghai) Information Consulting Co., Ltd.contact@imaios.cn/+86-13788973207
MR (Magnetic Resonance) arthrography of the shoulder: normal anatomy
- Antoine MICHEAU, MD , Denis HOA, MD
-
- Antoine MICHEAU, MD : 2 Allée Charles Darwin, 34170 Castelnau-le-lez
- Denis HOA, MD : 2 Allée Charles Darwin, 34170 Castelnau-le-lez
- Publication date: Dec 31, 2019 | Last update: Nov 24, 2025
- https://doi.org/10.37019/e-anatomy/691978 ISSN 2534-5079
This anatomical module of e-Anatomy is dedicated to the anatomy of the shoulder joint and the rotator cuff on a MR arthrography.
This MR arthrogram of the shoulder was performed on a male patient on a GE Signa Pioneer 3T MRI by Dr. Corey Chakarun from Shin Imaging in California. The exam is not normal because of a chronic injury of the anteroinferior glenoid labroligamentous complex.
An injection of 12ml gadolinium solution (1:200 dilution) into the shoulder joint has been done under fluoroscopic guidance, with an anterior approach (patient in a supine position with the shoulder in slightly external rotation).
Then the MR was performed with the shoulder placed in a neutral position (except for the ABER), with 5 different sequences commonly used for MR arthrography of the shoulder joint:
- Axial T1-weighted fat saturation

- Oblique coronal T1-weighted fat saturation
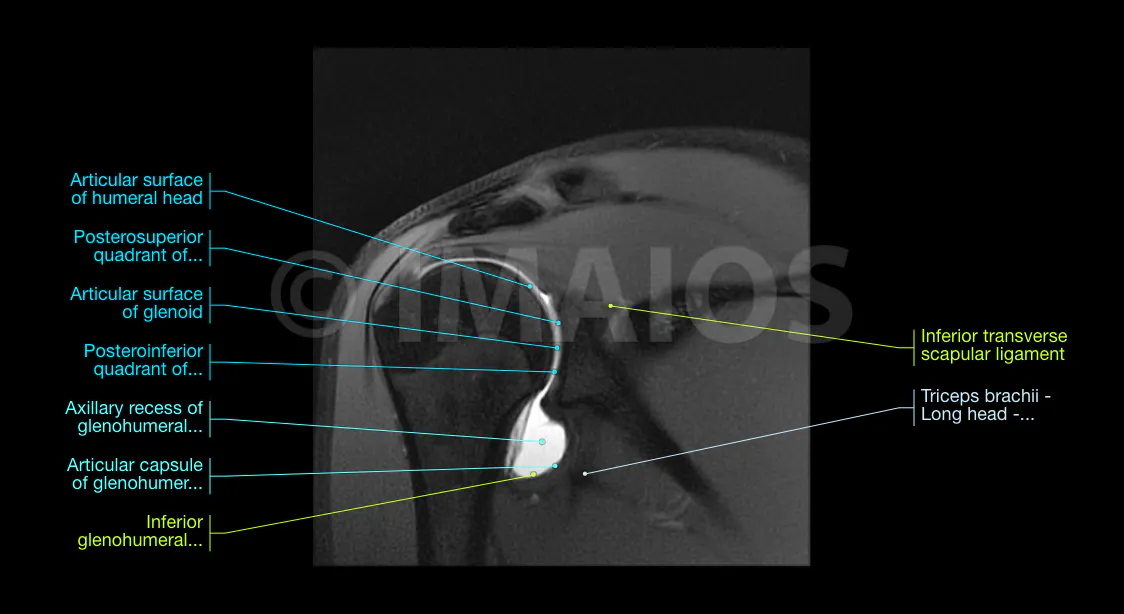
- Oblique coronal PD-weighted fat saturation
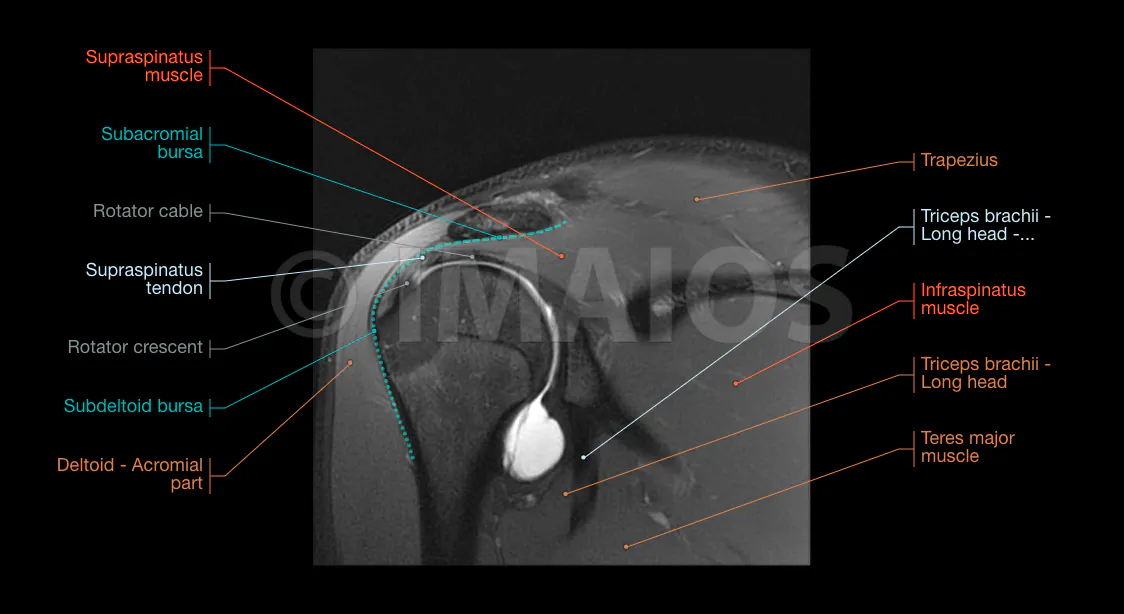
- Oblique sagittal T1-weighted FSE
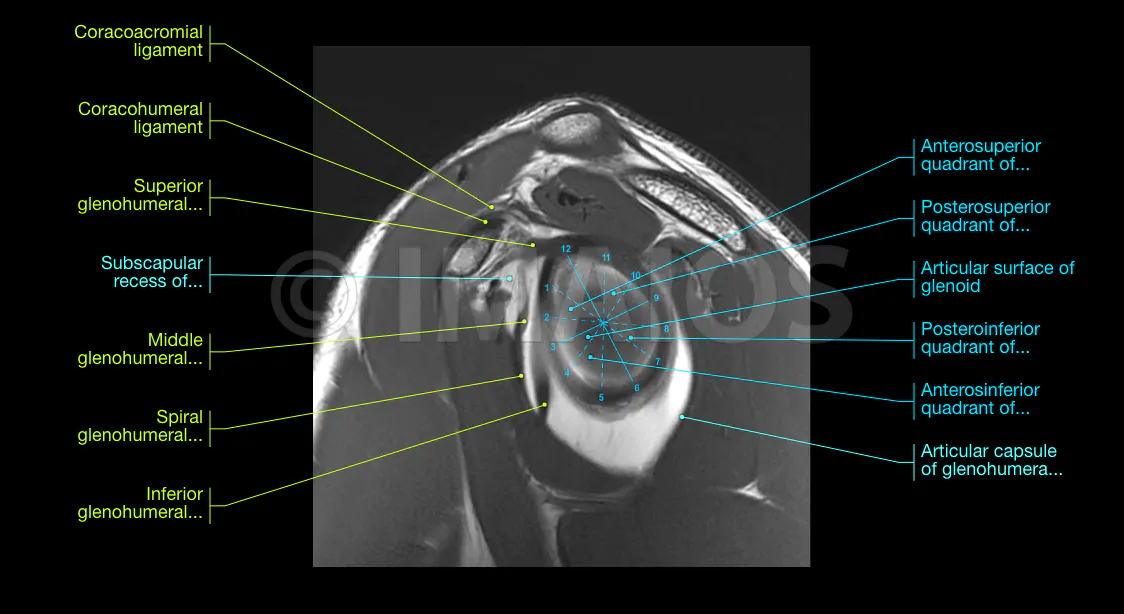
- T1-weighted fat saturation in abduction and external rotation (ABER)





- Normal Shoulder MRI and MR Arthrography: Anatomy and Technique. Seminars in musculoskeletal radiology.Llopis, Eva & Montesinos, Pau & Guedez, M & Aguilella, Luis & Cerezal, Luis. (2015). 19. 212-30. 10.1055/s-0035-1549316
- The anterior glenohumeral joint capsule: macroscopic and MRI anatomy of the fasciculus obliquus or so-called ligamentum glenohumerale spirale - Griffin N, Charles-Edwards G, Grant LA. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography: the ABC of MRCP. Insights Imaging. 2012;3(1):11–21. doi:10.1007/s13244-011-0129-9
- Transverse Thickening Along the Articular Surface of the Rotator Cuff Consistent With the Rotator Cable: Identification With MR Arthrography and Relevance in Rotator Cuff Evaluation. Kenneth Sheah, Miriam A. Bredella, Jon J. P. Warner, Elkan F. Halpern, and William E. Palmer American Journal of Roentgenology 2009 193:3, 679-686
- Terminologia anatomica: international anatomical terminology By the Federative Committee on Anatomical Terminology (FCAT). Stuttgart: Georg Thieme Verlag. ISBN-10: 3-13-114361-4. ISBN-13: 978-3-13-114361
No content available

